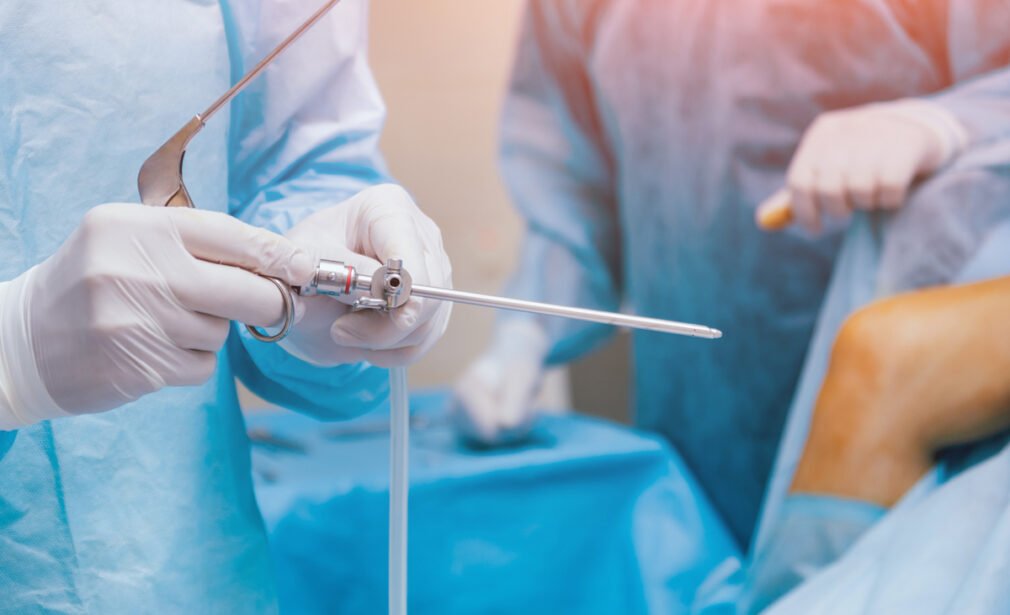
Arthroscopy Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that orthopedic surgeons use to diagnose and treat joint disorders. The best arthroscopy surgeon in Ahmedabad is a highly skilled and trained medical professional who specializes in performing arthroscopic procedures on patients.
As an Arthroscopy Surgeon in Ahmedabad, the first step in my process is to conduct a thorough examination of the patient’s joint using advanced imaging technologies, such as MRI or CT scans. Once the problem is identified, the arthroscopy doctor in Ahmedabad uses a small camera known as an arthroscope, which is inserted into the joint through a small incision. The camera allows us to see inside the joint and perform a range of procedures, including the repair of damaged cartilage or ligaments, removal of bone spurs, and trimming of damaged tissue.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat joint problems. It involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the joint through tiny incisions, allowing the surgeon to view the inside of the joint on a monitor. It is commonly performed on joints such as the knee, shoulder, elbow, hip, ankle, and wrist. The procedure helps diagnose issues like cartilage damage, ligament tears, and inflammation, and can also be used to treat these problems.
Best Arthroscopy Surgeon in Ahmedabad
Arthroscopy is a non-invasive surgery that can be employed to identify and treat joint disorders. The procedure can address a variety of issues, which include arthritis, sports injuries, and ligament tears. If you’re looking for a skilled arthroscopy surgeon in Ahmedabad and the surrounding areas, you must choose an experienced professional with years of experience in the field. The camera sends pictures of the interior of the joint to the video monitor. This allows the surgeon to detect defects or anomalies. In the course of the surgery, the surgeon may also insert tiny instruments inside the joint to fix or remove injured tissue.
The most advanced HD Arthroscopy system with completely new equipment and devices for the most effective treatment. Our team includes highly skilled arthroscopic surgeons and the arthroscopy physician for Arthroscopic procedures and orthopaedic treatment of shoulder and knee injuries, accidents, and injuries of other injuries. Dr. Tirth Vyas is one of the top arthroscopy surgeon Ahmedabad. His main areas of expertise are the field of Arthroscopic surgery and sports injury, Arthroplasty, Complex ligament reconstruction.
Why Choose Dr. Tirth Vyas For Arthroscopy Surgeon in Ahmedabad?
Dr. Tirth Vyas is known as one of the best arthroscopy surgeon in Ahmedabad, working as an orthopedic physician for ten more years. He’s obtained the required qualifications, expertise, as well as the skills to perform various orthopedic open or surgical procedures using arthroscopic techniques in Ahmedabad.
He is a highly acclaimed surgeon who is an arthroscopy surgeon. Who has extensive expertise in arthroscopy surgery? He has a specialization in arthroscopy surgery that includes surgery to treat ACL reconstruction, rotator-cuff repair, and meniscus repair. Also, he is known for his experience in the treatment of complicated knee and shoulder problems, such as the knee ligament, shoulder instability reconstruction, osteoarthritis, as well as cartilage injuries. His expertise in surgery and his experience are lauded by a lot of patients. This makes him a top choice to receive arthroscopy treatment in Ahmedabad.
Best Knee Arthroscopy Doctor in Ahmedabad
Are you searching for the best knee arthroscopy doctor in Ahmedabad? Do you think so? Dr. Tirth Vyas is board board-certified knee arthroscopy doctor in Ahmedabad. Dr. Tirth Vyas is an acclaimed surgeon and orthopedic doctor practising in Ahmedabad. He is a doctor with more than 10 years of experience. Arthroscopic surgery can be described as a minimally invasive technique for the diagnosis and treatment of joint pain, providing better therapeutic advantages. This procedure is suggested to treat joint problems such as injuries, inflammation, pain, or wear and tear. It can be performed at any ligament, joint, or tendon.
The procedure provides a more precise understanding of the region to be treated. This procedure utilizes an instrument that is known as an arthroscope, which has tiny cameras to see the desired area for treatment. By making a few tiny incisions, specially-designed instruments are introduced to carry out the necessary repairs to the joint. Contrary to conventional open surgery, the arthroscopic procedure allows orthopedic surgeons to use smaller cuts, resulting in little or no injury to the tissue. In the end, patients who have arthroscopic surgery suffer less pain post-operatively.
Guidelines for Choosing the Best Arthroscopy Hospital in Ahmedabad?
The right choice of an institution for an arthroscopy procedure is vital since it greatly impacts the outcome of the procedure and the general experience of the patient. Dr. Tirth Vyas is the best hospital for arthroscopy hospital in Ahmedabad. There are some things you should be aware of when picking an arthroscopy specialist:
- Choose a medical facility with an appropriate level of accreditation and qualifications for orthopedic surgery.
- Choose a surgeon who specializes in arthroscopy, with experience in modern treatment methods.
- Read testimonials from patients, since they will provide details on positive experiences and successful procedures.
- Verify the health of the hospital where the operation will be carried out. Verify that the facility or clinic is modernized with cutting-edge technology regarding treatments and diagnosis methods within the orthopedic area.
- Find a surgeon who takes the time to explain diagnosis, the treatment options, as well as the anticipated outcomes clearly and concisely.
Common Conditions Treated With Knee Arthroscopy Surgeon in Ahmedabad Include:
- Repair or removal of damaged meniscal cartilage
- Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament
- Remove loose fragments of cartilage or bone.
Incisions are then closed using sutures, staples, or threads. For the best knee arthroscopy in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, take a look at scheduling appointments with Dr. Tirth Vyas, an expert orthopedic surgeon and a best knee arthroscopy surgeon in Ahmedabad.
Best Knee Arthroscopy in Ahmedabad
Dr. Tirth Vyas is a well-known arthroscopy surgeon who has a specialization in knee arthroscopy in Ahmedabad. He has performed surgeries on numerous athletes and has an extensive client base both throughout Ahmedabad as well as around the world. Dr. Tirth Vyas has conducted thousands of procedures over more than two years. He can treat injuries to ligaments and meniscal tears and early osteoarthritis, as well as numerous other ailments that affect the knee, using an arthroscopy. Additionally, he performs arthroscopy on different joints, such as the elbow, shoulder, ankle, and ankle. As needed.
He has written numerous research papers that have been published in National as well as International Orthopaedic Journals. Because of his knowledge in the field and his expertise, he has been invited to numerous public forums for talks on how to prevent injuries to the shoulder and knee. He has accumulated a wealth of expertise in the field of arthroscopy because of his extensive knowledge, which is essential to achieving success with this procedure. Additionally, he has made investments in the most modern and modern arthroscopy technology in the most advanced operating theatres.
Various Types of Arthroscopy Surgery
ACL Reconstruction Surgery
This type of surgery is commonly performed on athletes and active individuals who have sustained a knee injury while playing sports or engaging in other physical activities. During ACL reconstruction surgery, the damaged ligament is detached and replaced with a new ligament. This can be done using a variety of different techniques, including autografts (using tissue from the patient’s own body) or allografts (using tissue from a donor).
The surgery is normally performed under general anesthesia and can take several hours to complete. With Knee Arthroscopy Surgeons in Ahmedabad, patients will need to undergo a period of rehabilitation & physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the affected knee.
Shoulder Arthroscopic Surgery
Shoulder arthroscopic surgery can be used to treat a range of conditions, including rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, shoulder instability, and frozen shoulder. This surgery is often recommended when conservative treatments such as physical therapy and medication have failed to provide relief.
Bankart Repair
Bankart repair is a surgical procedure used to treat shoulder instability caused by anterior dislocation of the humeral head. The procedure involves repairing the damaged ligaments and reattaching them to the bone to stabilize the shoulder joint.
Bankart repair has a high success rate and can significantly improve shoulder stability and function. It is a preferred treatment option for athletes and active individuals who engage in activities that require repetitive overhead motions, such as throwing or serving.
Rotator Cuff Repair
Rotator cuff repair is a surgical procedure that aims to repair the damaged or torn tendons in the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff is a group of 4 muscles and their associated tendons that connects the shoulder blade to the upper arm bone. These muscles and tendons work together to help lift and rotate the arm, allowing us to perform various daily activities. However, due to overuse or injury, the tendons in the rotator cuff can become damaged or torn, causing pain and limited mobility. The aim of rotator cuff repair surgery is to restore function and alleviate pain in the shoulder joint.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy may be recommended when a joint condition is suspected but not clearly diagnosed using non-invasive imaging techniques (e.g., X-rays, MRIs), or when joint pain persists despite conservative treatments. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent joint pain: Pain that does not improve with rest, medications, or physical therapy.
- Swelling: Chronic swelling or fluid buildup within the joint.
- Joint stiffness: Limited range of motion, difficulty bending or straightening the joint.
- Joint instability: The sensation that the joint is unstable or may “give way” during movement.
- Clicking or catching sensation: Feeling of the joint catching or locking during movement, often due to cartilage tears or loose bodies.
- Loss of function: Difficulty performing routine activities due to joint pain or mechanical dysfunction.
Causes of Joint Damage Requiring Arthroscopy
Several joint conditions can lead to pain, swelling, and dysfunction that may require arthroscopy for diagnosis and treatment:
- Torn cartilage: Damage to the cartilage in the joint (e.g., meniscus tears in the knee, labral tears in the shoulder or hip) is a common cause of pain and instability.
- Ligament tears: Partial or complete ligament tears, such as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear in the knee.
- Synovitis: Inflammation of the synovial membrane that lines the joint, often seen in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Loose bodies: Pieces of bone, cartilage, or tissue floating within the joint, causing pain or locking.
- Joint infection: Arthroscopy may be used to clean out infected tissue and drain fluid from the joint.
- Joint impingement: Bony growths or deformities that cause pinching of the joint during movement (e.g., shoulder impingement).
- Degenerative joint diseases: Conditions such as osteoarthritis, where the cartilage wears away, leading to joint damage.
Procedure of Knee Arthroscopy in Ahmedabad
Arthroscopy is usually performed under general or local anesthesia, depending on the joint being examined or treated. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Incision: Small incisions (about the size of a buttonhole) are made around the joint.
- Insertion of arthroscope: The arthroscope, a small camera attached to a thin tube, is inserted into the joint through one of the incisions. The camera displays images of the joint interior on a monitor.
- Diagnosis and treatment: Depending on the condition, the surgeon may use specialized tools inserted through additional incisions to remove damaged tissue, repair cartilage or ligaments, or clean out the joint.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with stitches or surgical tape, and a dressing is applied to the joint.
Recovery and Post-Surgery Physiotherapy
Recovery from arthroscopy is typically faster than from traditional open surgery. However, the recovery process depends on the joint treated and the extent of the procedure.
Phase 1 (First 1–2 Weeks Post-Op)
- Goals: Reduce pain and swelling, protect the joint, and restore gentle movement.
- Treatment:
- Use of ice packs to manage swelling.
- Compression bandages and elevation to reduce swelling.
- Pain management with medications as prescribed.
- Gentle range-of-motion (ROM) exercises to prevent stiffness and improve mobility, guided by a physiotherapist.
- Walking with crutches or using a brace if weight-bearing is restricted (for knee or hip arthroscopy).
Phase 2 (2–6 Weeks Post-Op)
- Goals: Improve joint mobility, strengthen muscles, and increase activity levels.
- Exercises:
- Gradual progression of ROM exercises to restore full joint flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles surrounding the joint to improve stability (e.g., quadriceps and hamstring exercises for knee arthroscopy, rotator cuff exercises for shoulder arthroscopy).
- Balance and proprioception exercises to enhance joint control.
- Low-impact activities such as stationary cycling or swimming to improve joint mobility without stressing the joint.
Phase 3 (6–12 Weeks Post-Op)
- Goals: Restore strength, balance, and joint function for daily activities.
- Exercises:
- Advanced strengthening exercises using resistance bands, weights, or body weight.
- Functional exercises like squats, step-ups, and lunges to improve joint strength and flexibility.
- Sport-specific or activity-specific exercises for athletes, focusing on returning to their previous level of performance.
- Progressive increase in activity, including walking, jogging, or light sports activities.
Recovery Timeline
- Return to daily activities: Patients can usually resume basic activities within a few days to a week, depending on the joint treated.
- Return to work: Sedentary work can often be resumed in 1–2 weeks, while physically demanding jobs may take 4–6 weeks.
- Return to sports: Most patients can return to low-impact sports within 6–8 weeks, though high-impact sports may take 3–6 months, depending on the joint and type of surgery.
Non-Surgical Alternatives to Arthroscopy
Before arthroscopy, non-surgical options may be tried to manage joint symptoms:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A customized exercise program to improve joint strength and mobility.
- Corticosteroid injections: Used to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
- Joint aspiration: Draining excess fluid from the joint to reduce swelling and pain.
- Activity modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate joint pain and modifying daily routines to reduce joint stress.
Potential Risks and Complications
While arthroscopy is minimally invasive, it carries some risks, including:
- Infection: Though rare, infection may occur at the incision site or within the joint.
- Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may develop, particularly in lower limb surgeries.
- Joint stiffness: Some patients may experience stiffness or limited motion after surgery.
- Nerve or blood vessel damage: The small instruments used in arthroscopy may inadvertently cause nerve or blood vessel injury.
- Failure to relieve symptoms: In some cases, arthroscopy may not fully resolve the underlying issue.
Arthroscopy is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating various joint conditions. With its minimally invasive nature, patients often experience quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. A structured physiotherapy program is essential for restoring joint function, mobility, and strength after surgery, allowing patients to return to their normal activities or sports.
Dr. Tirth Vyas aims to offer top Arthroscopy Surgeon Ahmedabad for his patients and a treating them as a family. Consult him today for any broken or injuries in your joints.